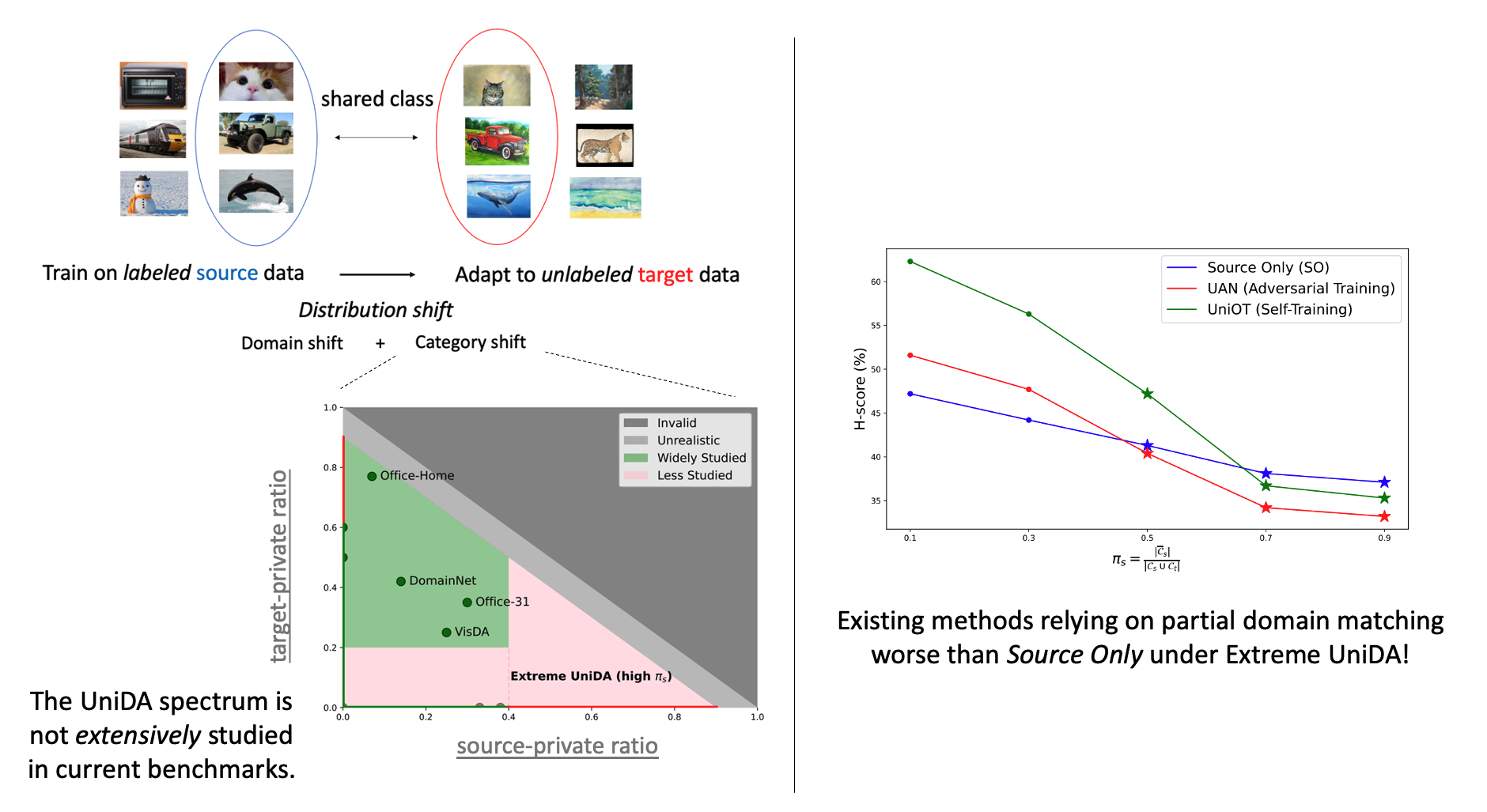
Abstract
Universal Domain Adaptation (UniDA) addresses unsupervised domain adaptation where target classes may differ arbitrarily from source ones, except for a shared subset. A widely used approach, partial domain matching (PDM), aligns only shared classes but struggles in extreme cases where many source classes are absent in the target domain, underperforming the most naive baseline that trains on only source data. In this work, we identify that the failure of PDM for extreme UniDA stems from dimensional collapse (DC) in target representations. To address target DC, we propose to jointly leverage the alignment and uniformity techniques in self-supervised learning on the unlabeled target data to preserve the intrinsic structure of the learned representations. Our experimental results confirm that SSL consistently advances PDM and delivers new state-of-the-art results across a broader benchmark of UniDA scenarios with different portions of shared classes, representing a crucial step toward truly comprehensive UniDA.
Video
Motivation
Key Findings
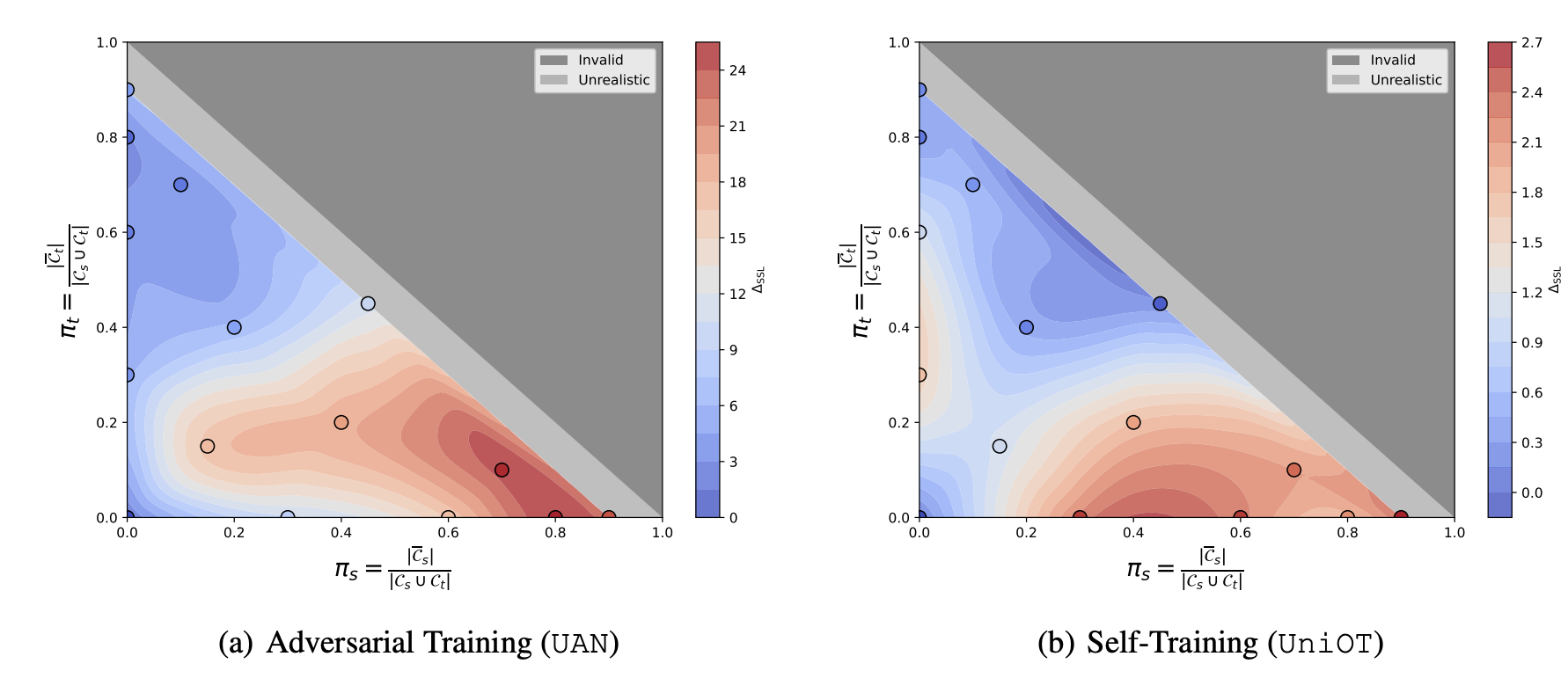
Dimensional Collapse under Extreme UniDA
Our analysis reveals that dimensional collapse occurs when the source-private ratio is high. We demonstrate this phenomenon through both a toy example for intuitive visualization and rigorous analysis of singular value spectrum.
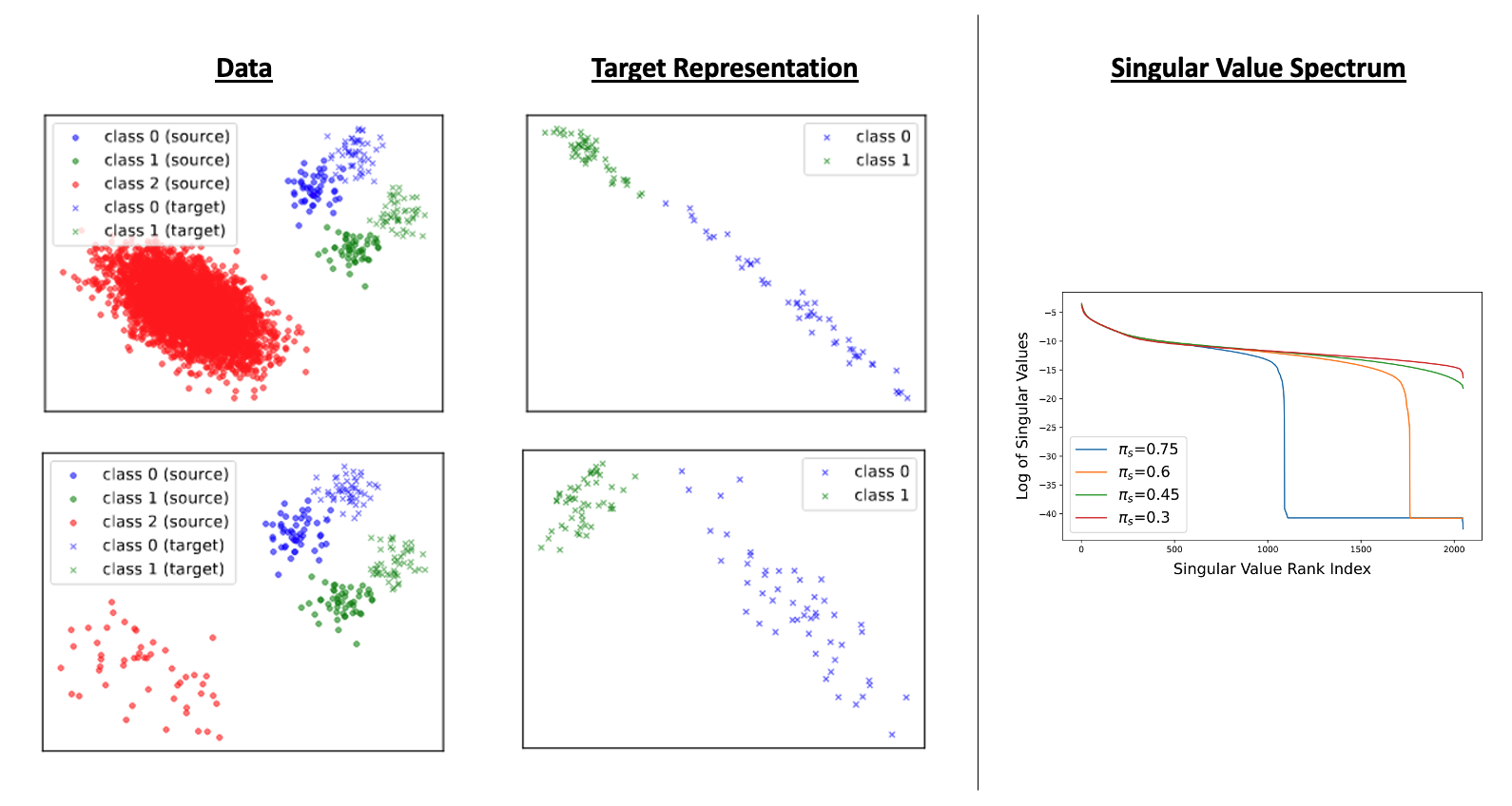
Degraded Representation Quality Impairs PDM
Our analysis reveals that dimensional collapse occurs when the source-private ratio is high. We demonstrate this phenomenon through both a toy example for intuitive visualization and rigorous analysis of singular value spectrum.
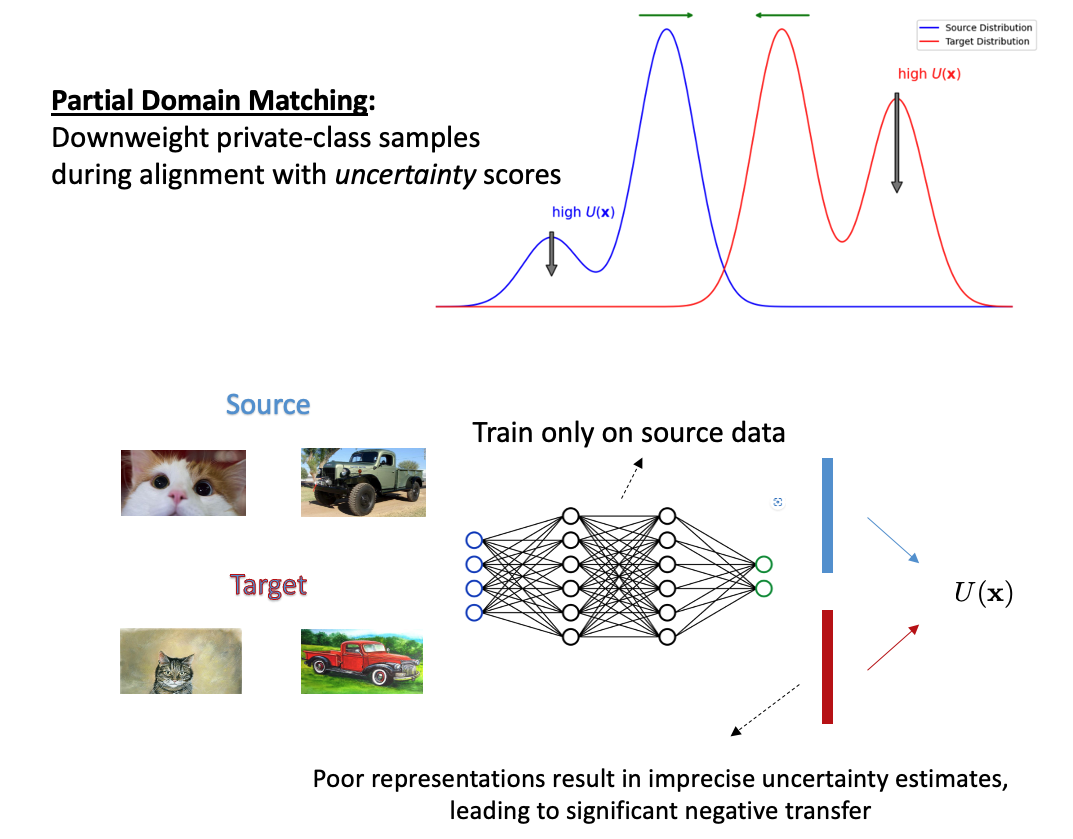
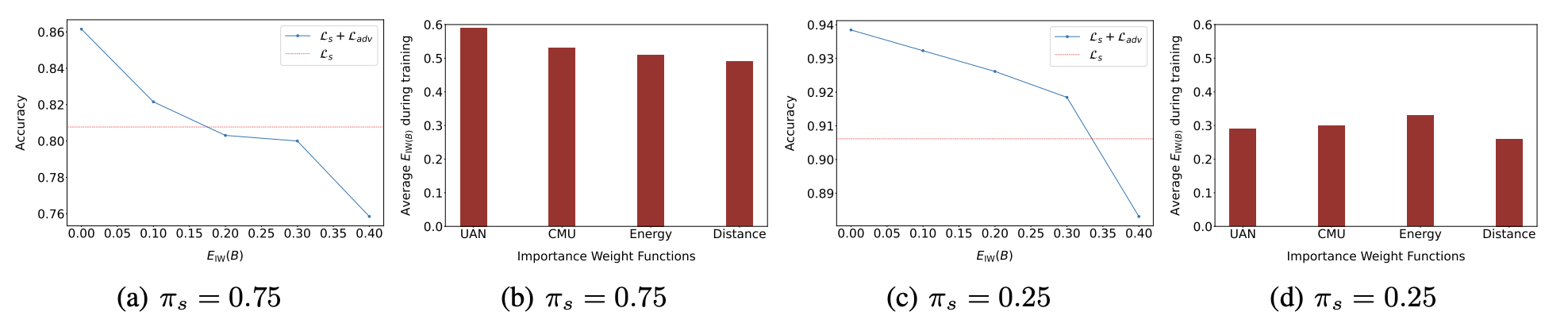
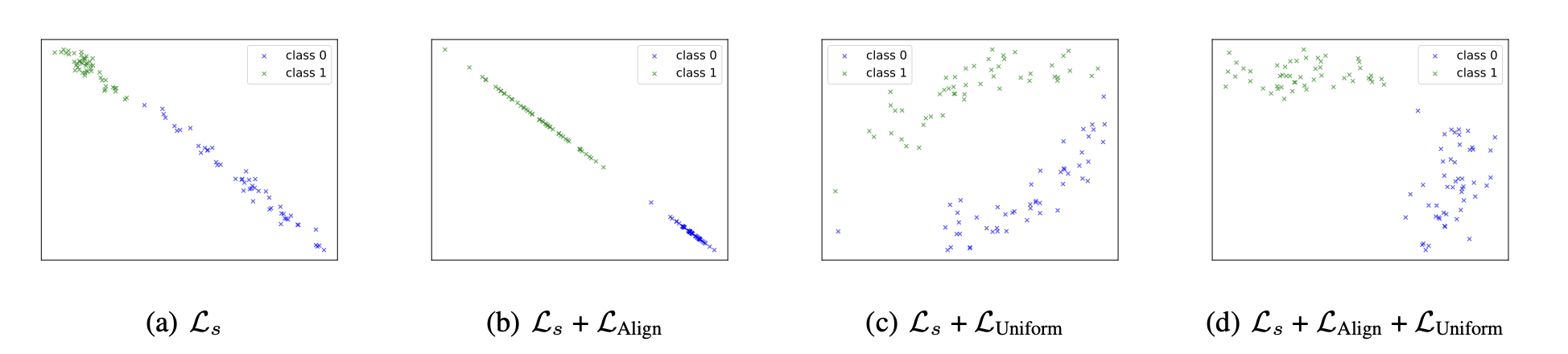
Address Dimensional Collapse without Labels
De-collapse Techniques from Self-Supervised Learning
Dimensional collapse is a well-known issue in self-supervised learning, primarily caused by the contrastive alignment term (Li et al., 2020). Various methods have been developed to address this problem, including contrastive learning approaches (e.g., AlignUniform, SimCLR), asymmetric models (e.g., SimSiam, BYOL), and redundancy reduction techniques (e.g., VICReg, Barlow Twins). Here, we show how the uniformity term from self-supervised learning can effectively prevent DC in UniDA. We further show that these SSL approaches also work in the paper.
BibTeX
@inproceedings{dcunida_fang2025,
title={Tackling Dimensional Collapse toward Comprehensive Universal Domain Adaptation},
author={Hung-Chieh Fang and Po-Yi Lu and Hsuan-Tien Lin},
booktitle={Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML)},
year={2025},
}